TOMCAT-CORE
Intro(TOMCAT-CORE) #
tomcat.version = 8.5.35
offical git repo | tag = 3.5.35 learning git repo
tomcat-8.5-doc
download 8.5.35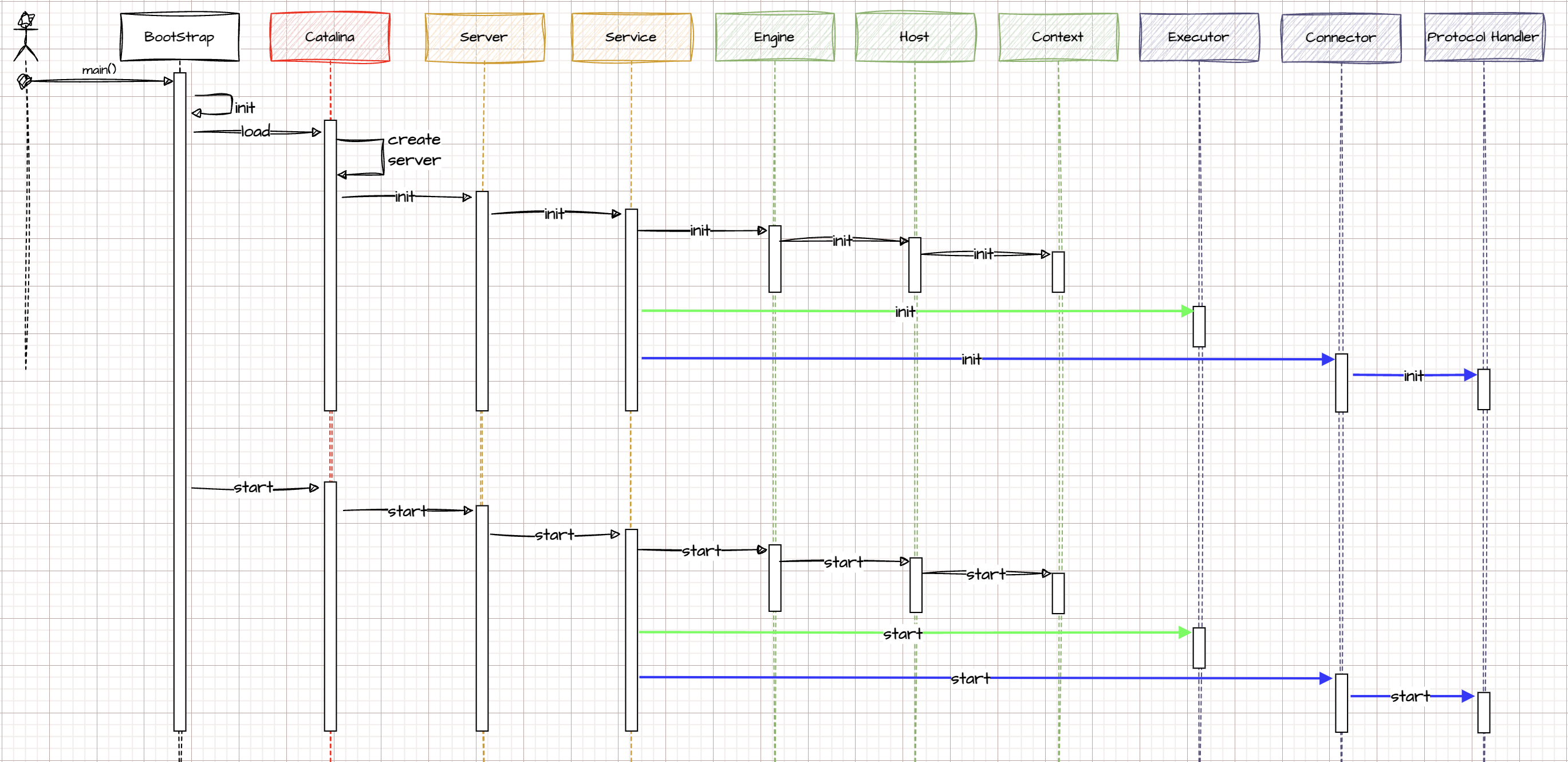
概念解释 #
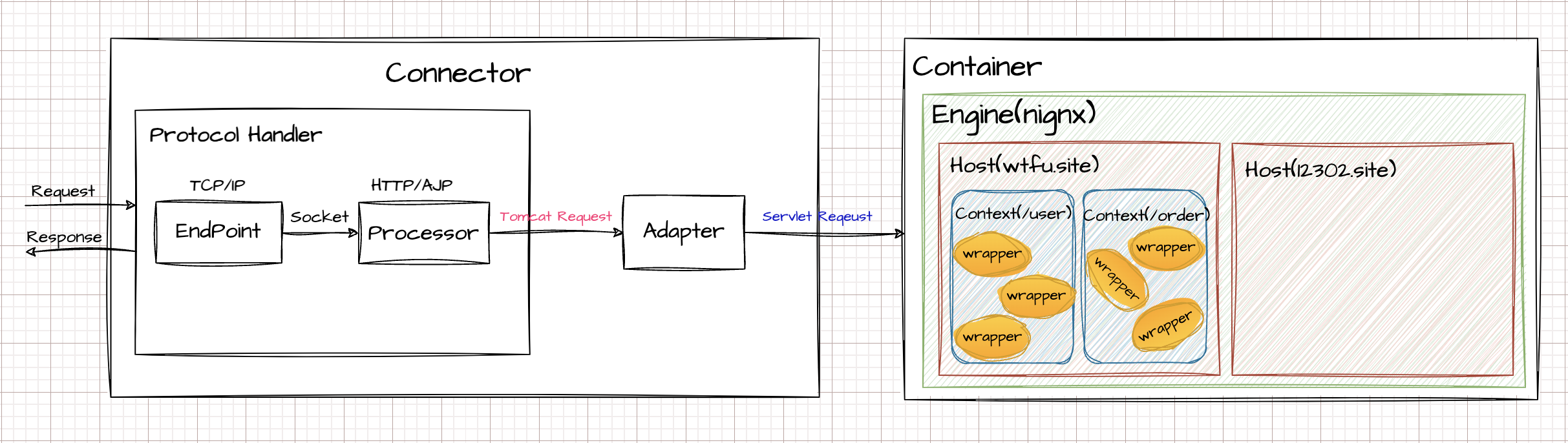
整体架构 #
Connector(【coyote】处理socket连接,负责网络字节流)
Container(【Catalina】加载servlet处理具体请求)启动流程 #
先是初始化
BootStrap->Calaline->Server->Service
BootStrap->Calaline->Server->Service->[Engine->Host->Context]
BootStrap->Calaline->Server->Service->[Executor]
BootStrap->Calaline->Server->Service->[ProtocalHandler]
然后调用start启动整个tomcatI/O模型和协议 #
BIO,NIO,AIO(NIO2),APR
HTTP/1.1,HTTP/2,AJP(用于和apache服务器集成用来处理静态资源)Jasper引擎 #
index.jsp -> jspServlet(找到文件) -> 渲染成servlet.class-> 加载调用
Context #
官方不建议直接在server.xml中配置,因为,server.xml文件只会在tomcat重新的时候重新加载。
- In an individual file at /META-INF/context.xml inside the application files
- In individual files (with a “.xml” extension) in the $CATALINA_BASE/conf/[enginename]/[hostname]/ directory
- Inside a Host element in the main conf/server.xml.
安全 #
1).删除webapp下面的管理页面和其他项目2).禁用server-user.xml里面的权限或者直接删除3).修改tomcat默认关机指令,或者禁用4).配置错误页面。JK protocol #
类加载器 #
MISC #
SynchronizedQueue<T> #
Note
提供一个同步队列,使用数组实现,用insert,remove控制边界,可以循环使用。默认
size=128。SynchronizedStack<T> #
SharedExecutor #
在
server.xml中配置的<Executor>标签, 引用 中的executor属性。
A reference to the name in an Executor element. If this attribute is set, and the named executor exists, the connector will use the executor, and all the other thread attributes will be ignored. Note that if a shared executor is not specified for a connector then the connector will use a private, internal executor to provide the thread pool.
解析赋值在org.apache.catalina.startup.ConnectorCreateRule#begin中。InternalExecutor #
内部线程池参数解读 ,参考 文档的Connector标准实现 部分。
1).minSpareThreads(最小备用线程数): The minimum number of threads always kept running. This includes both active and idle threads. If not specified, the default of 10 is used. If an executor is associated with this connector, this attribute is ignored as the connector will execute tasks using the executor rather than an internal thread pool. Note that if an executor is configured any value set for this attribute will be recorded correctly but it will be reported (e.g. via JMX) as -1 to make clear that it is not used.2).maxThreads: The maximum number of request processing threads to be created by this Connector, which therefore determines the maximum number of simultaneous requests that can be handled. If not specified, this attribute is set to 200. If an executor is associated with this connector, this attribute is ignored as the connector will execute tasks using the executor rather than an internal thread pool. Note that if an executor is configured any value set for this attribute will be recorded correctly but it will be reported (e.g. via JMX) as -1 to make clear that it is not used.外部控制值的配置:
<Connector port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1" executor="tomcatThreadPool123" minSpareThreads="12"
大致原理就是通过自省的IntrospectionUtils工具进行赋值:Connector#setProperty() --> AbstractProtocol#setMinSpareThreads() --> endpoint#setMinSpareThreads();TaskQueue_任务队列 #
getHandler() #
Reference #
- https://github.com/apache/tomcat/tree/8.5.35
- https://github.com/12302-bak/tomcat-analysis
- https://tomcat.apache.org/tomcat-8.5-doc/introduction.html
- https://archive.apache.org/dist/tomcat/tomcat-8/v8.5.35/
- https://tomcat.apache.org/connectors-doc/ajp/ajpv13a.html 【AJP protocol introduce】 【AJP protocol CVE】
- https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1dJ411N7Um
- https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000023475177
- tomcat启动类中使用反射调用的意义
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/7672466/why-does-tomcat-use-reflection-for-catalina-instancilization
- 以下是源码调试环境搭建
- https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1dJ411N7Um?p=5
- https://www.cnblogs.com/kukuxjx/p/17701288.html
- https://www.cnblogs.com/grasp/p/10061577.html
- https://www.cnblogs.com/LiPengFeiii/p/15228789.html
- https://blog.csdn.net/xuan_lu/article/details/106314487