03_DQL
DQL语言的学习 #
1.基础查询 #
语法:
select 查询列表 from 表名;
特点:
1,查询列表可以是:表中的字段,常量值,表达式,函数
2,查询的结果是一个虚拟的表格
1.查询表中的单个字段select last_name from employees limit 10;
2.查询表中的多个字段select last_name, salary, email from employees limit 10;
3.查询表中的所有字段select * from employees limit 10;
4.查询常量值select 100;,select 'john';
5.查询表达式select 100%98;
6.查询函数select version();
7.起别名
① 便于理解,② 如果查询字段有重名,使用别名可以区分开来,③ 别名中有特殊字符使用引号扩起来select 100%98 as 结果;select last_name as 姓,first_name as 名 from employees limit 10;
8.去重
# case: 查询员工表中涉及到的所有的部门编号select distinct department_id from employees;
9.+号的作用 ① 仅仅只有一个功能,运算符select 100 + 90;连个操作数都为数值型,则做加法运算select '123' + 90;213 其中一个为字符型,可以转换,做加法运算select 'john' + 9090 转换失败,则将字符型数值转换成 0 再做加法。select null + 10;NULL 只要有一方为NULL, 则结果肯定为NULL。
所以下面字符串连接得使用concat函数
case: 查询员工名和姓连接成一个字段,并显示为姓名select concat(last_name,first_name) as 姓名 from employees limit 10;2.条件查询 #
语法:
select 查询列表 from 表名 where 筛选条件;
分类:
1,按条件表达式筛选:简单条件运算符>,<,=,!=,<>,>=,<=,<=>(安全等于)可以与NULL进行判断。
2,按逻辑表达式筛选:逻辑运算符&&,||,!,and,or,not
3,模糊查询:like,between and,in,is null
一、按条件表达式查询
case1: 查询工资 > 12000 的员工信息select * from employees where salary > 12000;
case2: 查询部门编号 不等于90 号的员工名和部门编号select last_name, department_id from employees where department_id != 90;
二、按逻辑表达式查询
case1: 查询工资在 10000-20000之间的员工名,工资及奖金select last_name, salary, commission_pct from employees where salary >= 10000 and salary <= 20000;
case2: 查询部门编号不是在90~110之间,或者工资高于15000 的员工信息select * from employees where department_id < 90 or department_id > 110 or salary > 15000;select * from employees where not(department_id >= 90 and department_id <= 110) or salary > 15000;
三、模糊查询
like-case1: 查询员工名中包含字符a的员工信息select * from employees where last_name like '%a%';
like-case2: 查询员工名中第三个字符为n,第五个字符为l的员工名和工资select last_name, salary from employees where last_name like '__n_l%';
like-case3: 查询员工名中第二个字符为_的员工名select last_name from employees where last_name like '_\_%';select last_name from employees where last_name like '_$_%' escape '$';
between-and-case1: 查询员工编号在100-120之间的员工信息select * from employees where employee_id between 100 and 120;
in-case1: 查询员工的工种编号是 IT_PROG,AD_VP,AD_PRES中的一个员工名和工种编号select last_name, job_id from employees where job_id in ('IT_PROT', 'AD_VP', 'AD_PRES');
is-null-case1: 查询(没有|有)奖金的员工名和奖金率select last_name, commission_pct from employees where commission_pct is null;select last_name, commission_pct from employees where commission_pct is not null;3.排序查询 #
语法:
select 查询列表 from 表名 [where 筛选条件] order by 排序列表 [asc|desc];
特点:
1,asc代表的是升序,desc代表的是降序,如果不写,默认是升序。
2,order by 子句中可以支持单个字段,多个字段,表达式,函数,别名。
3,order by 子句一般是放在查询语句的最后面,limit子句除外。
case1: 查询员工信息,要求工资(从高到低|从低到高)排序select * from employees order by salary desc;select * from employees order by salary;
case2: 查询部门编号 >=90 的员工信息,按入职时间的先后进行排序【添加筛选条件】select * from employees where department_id >= 90 order by hiredate asc;
case3: 按年薪的高低显示员工的信息和年薪【按(表达式|别名)排序】select *, salary * 12 * ( 1 + ifnull(commission_pct, 0)) as 年薪 from employees order by 年薪 desc;
case4: 按姓名的长度显示员工的姓名和工资【按函数排序】select length(last_name) 字节长度, last_name, salary from employees order by 字节长度 desc;
case5: 查询员工信息,要求先按照工资排序,再按照员工编号排序【按多个字段排序】select * from employees order by salary asc, employee_id desc;4.常见函数 #
语法:
select 函数名(实参列表) [from 表名];
函数帮助:help substr;
以下都是单行函数
特点:1,叫什么(函数名) 2,干什么(函数功能)
好处:1,隐藏了实现的细节 2,提高代码的重用性
分类:单行函数,分组函数(做统计用,又称为统计函数,聚合函数,组函数)一、字符函数 #
Note
一、length()获取参数值的字节个数,和字符集有关系
select length('John');select length('张三丰hahaha');
二、concat() 拼接字符串select concat(last_name, '_', first_name) 姓名 from employees;
三、upper(), lower() 大小写转换select concat(upper(last_name), '_', lower(first_name)) 姓名 from employees;
四、substr(), substring() 字符串截取select substr('李莫愁爱上了陆展元', 7) out_put;select substr('李莫愁爱上了陆展元', 1, 3) out_put;
case1: 姓名中首字符大写,其他字符小写然后用_拼接,显示出来select concat(upper(substr(last_name, 1, 1)), '_', lower(substr(last_name, 2))) out_put from employees;
五、instr() 返回子串第一次出现的索引,如果找不到返回0select instr('杨不殷六侠悔爱上了殷六侠', '殷六侠') out_put;select instr('杨不殷六侠悔爱上了殷六侠', '殷八侠') out_put;
六、trim() 去前后空格select length(trim(' 张翠山 ')) out_put;select trim('a' from 'aaaaahello a cworldaaaaaaa') out_put;
七、lpad(),rpad() 用指定的字符实现左,右填充指定长度select lpad('殷素素', 10, '*') out_put;select rpad('殷素素', 12, '*') out_put;
八、replace() 全部替换select replace('张无忌第一次碰见周芷若就爱上了周芷若','周芷若', '赵敏') out_put;二、数学函数 #
Note
一、round() 四舍五入
select round( 1.65);// 2select round( 1.45);// 1select round(-1.55);// -2select round(1.567, 2);// 1.57
二、ceil() 向上取整,返回 >= 该参数的最小整数select ceil( 1.52);// 2select ceil(-1.02);// -1
三、floor() 向下取整,返回 <= 该参数的最大整数select floor( 9.99);// 9select floor(-9.99);// -10
四、truncate 截断select truncate(1.65, 1);// 1.6
五、mod 取余 mod(a,b) ==> a - a/b * bselect mod(-10, -3);// -1select mod(-10, 3);// -1select mod( 10, 3);// 1select mod( 10, -3);// 1三、日期函数 #
Note
一、now() 返回当前系统日期+时间
select now();// 2024-06-06 07:03:35
二、curdate() 返回当前系统日期,不包含时间select curdate();// 2024-06-06
三、curtime() 返回当前系统时间,不包含日期select curtime();// 07:05:20
四、获取自定的部分,年,月,日,小时,分钟,秒select year(now());select year('1998-1-01');select month(now());select monthname(now());// June
五、str_to_date() 将日期格式的字符串转换成指定格式的日期select str_to_date('9-13-1999', '%m-%d-%Y');// 1999-09-13
六、date_format() 将日期转成字符select date_format('2018/6/6','%Y年%m月%d日');// 2018年06月06日
四、其他函数 #
Note
select version();,select database();,select user();五、流程控制函数 #
Note
一、if()
select if(10 < 5, 'hello', 'world');
二、case()
语法一: case 表达式 when 常量1 then 显示值1 when 常量2 then 显示值2 … else 显示值else end
case1: 查询员工的工资,要求,部门号=30,工资为1.1倍:40,1.2:50,1.3select salary, department_id, case department_id when 30 then salary * 1.1 when 40 then salary * 1.2 when 50 then salary * 1.3 else salary end as after from employees;
语法二: case when 条件1 then 显示值 when 条件2 then 显示值 else 显示值 else end
case2: 查询员工的工资的情况,要求,工资大于20000,显示A, >15000:B,>10000:Cselect salary, case when salary > 20000 then 'A' when salary > 15000 then 'B' when salary > 10000 then 'C' else 'D' end as after from employees;
5.分组函数 #
语法:
select 函数名(实参列表) [from 表名];
功能:用作统计使用,又称为聚合函数或统计函数或组函数
分类:sum 求和,avg 平均值,max 最大值,min 最小值,count 个数
特点:1).sum,avg一般用于处理数值类型2).以上分组函数都忽略 NULL 值3).可以和 distinct 搭配实现去重的运算4).count函数的单独介绍: 一般使用count(*)用作统计行数5).和分组函数一同查询的字段要求是group by后的字段
一、简单的使用select sum(salary) from employees;select avg(salary) from employees;select min(salary) from employees;select max(salary) from employees;select count(salary) from employees;select sum(salary), avg(salary), min(salary), max(salary), count(salary) from employees;select sum(salary), round(avg(salary), 2), min(salary), max(salary), count(salary) from employees;
二、参数支持哪些类型select sum(last_name), avg(last_name) from employees;// 返回0,不报错,无意义select max(last_name), min(last_name), count(last_name) from employees;
三、忽略NULLselect sum(commission_pct), avg(commission_pct), sum(commission_pct) / 35, sum(commission_pct) / 109 from employees;select count(commission_pct) from employees;
四、和 distinct 搭配select sum(distinct salary), sum(salary) from employees;select count(distinct salary), count(salary) from employees;
五、count函数的详细介绍
MYISAM 中 count(*) 的效率高,
INNODB count(*),count(1) 差不多,但比count(field)要高一些。select count(salary) from employees;select count(*) from employees;//可以认为如果当前字段为NULL,会测试下一个select count(1) from employees;
六、和分组函数一同查询的字段有限制select employee_id, avg(salary) from employees;// 此处的 employee_id 没有任何意义。6.分组查询 #
语法:
select columnM, func(columnN) from 表名 [where 筛选条件] [group by colomnM] [order by 排序列表 [asc|desc]];
注意:查询列表比较特殊,要求是分组函数和group by 后出现的字段。
特点:1).分组查询中的筛选条件分为两类,分组前和分组后。也就是下文中的having解释2).group by 子句支持单个字段分组,多个字段分组(多个字段之间用逗号分隔开没有顺序要求),表达式或函数(用的较少)3).也可以添加排序(排序放在整个分组查询的最后)
技巧:①: 分组函数做条件肯定是放在having子句中②: 能用分组前筛选的,就优先考试使用分组前筛选(也就是where后面),关乎性能问题
引入、查询每个部分的平均工资select department_id, avg(salary) from employees group by department_id;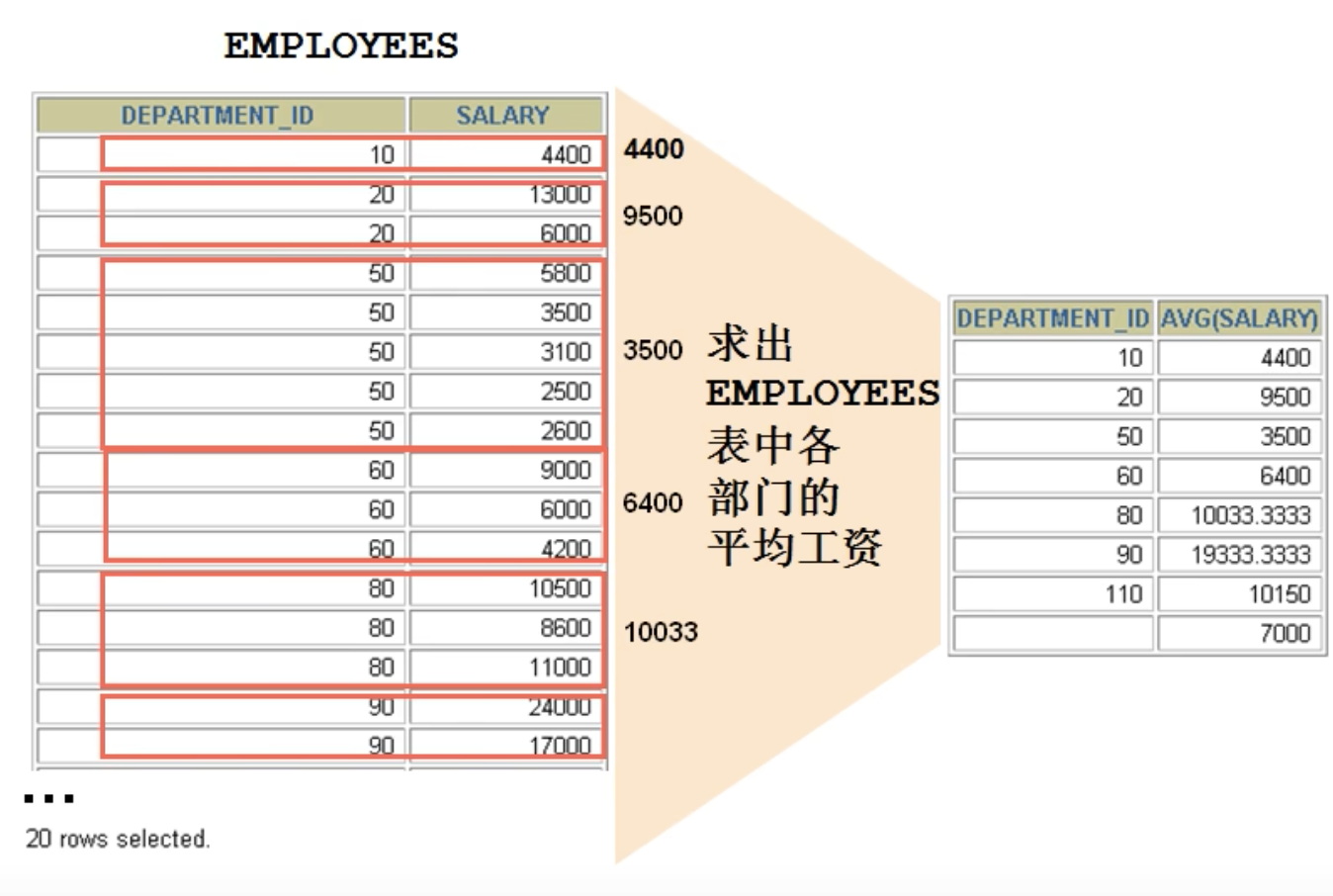
一、查询每个工种的最高工资select job_id, max(salary) from employees group by job_id;
二、查询每个部门上的部门个数select location_id, count(1) from departments group by location_id;
添加筛选条件
一、查询邮箱中包含a字符的,每个部分的平均工资select department_id, avg(salary) from employees where email like '%a%' group by department_id;
二、查询有奖金的每个领导手下员工的最高工资select manager_id, max(salary) from employees where commission_pct is not null group by manager_id;
添加复杂的筛选条件having: 与where相比,where作用在分组动作前,而having作用在分组动作后。
一、查询哪个部分的员工个数 > 2select department_id, count(1) AS _count from employees group by department_id having _count > 2;
二、查询每个工种有奖金的员工的最高工资>12000的工种编号和最高工资select job_id, max(salary) AS _max from employees where commission_pct is not null group by job_id having _max > 12000;
三、查询领导编号>102的每个领导手下的最低工资>5000的领导编号是哪个,以及其最低工资select manager_id, min(salary) _min from employees where manager_id > 102 group by manager_id having _min > 5000;
按表达式或函数分组
一、按员工姓名的长度分组,查询每一组的员工个数,筛选员工个数>5 的有哪些?select length(last_name) as _len, count(1) as _count from employees group by _len having _count > 5;
按多个字段分组
一、查询每个部门每个工种的员工的平均工资select department_id, job_id, avg(salary) from employees group by department_id, job_id;
添加排序
一、查询每个部门每个工种的员工的平均工资,并且按平均工资的高低显示select department_id, job_id, avg(salary) AS _avg from employees group by department_id, job_id order by _avg;7.连接查询 #
含义:又称多表查询,当查询的字段来自于多个表时,就会用到
连接查询
笛卡尔乘积现象:表1 有m行,表2,有n行,结果=m*n行。发生原因:没有有效的连接条件,添加条件可以避免。
分类:1).按年代分:sql92标准:仅仅支持内连接,sql99标准(推荐):支持内连接+外连接(左外+右外)+ 交叉连接2).按功能:内连接(等值连接,非等值连接,自连接),外连接(左外连接,右外连接,全外连接),交叉连接Note
一、sql92标准
语法:select 查询列表 from 表1 别名, 表2 别名 [where 筛选条件] [group by 分组] [having 筛选条件] [order by 排序列表 [asc|desc]];
特点:①: 多表等值连接的结果为多表的交集部分②: n表连接,至少需要n-1个连接条件③: 多表的顺序没有要求④: 一般需要为表起别名⑤: 可以搭配前面介绍的所有子句使用,比如排序,分组,筛选。
sql92.1 等值连接:
sql92.1.1 demo
case1: 查询女神名和对应的男神名select name, boyName from boys,beauty where boys.id = beauty.boyfriend_id;
case2: 查询员工名和对应的部门名select last_name, department_name from employees, departments where employees.department_id = departments.department_id;
sql92.1.2 为表起别名
①提高语句的简洁度,②区分多个重名的字段,注意:如果为表起别名,则查询字段就不能用原来的表名去限定了。
case1: 查询员工名,工种号,工种名select last_name, j.job_id,j.job_title from employees e, jobs j where e.job_id = j.job_id;
sql92.1.3 两个表的顺序可以调换
case1: 查询员工名,工种号,工种名select last_name, j.job_id,j.job_title from jobs j, employees e where e.job_id = j.job_id;
sql92.1.4 可以添加筛选
case1: 查询有奖金的员工名,部门名select last_name, department_name, commission_pct from employees e, departments d where e.department_id = d.department_id and e.commission_pct is not null;
case2 : 查询城市名中第二个字符为o的部门名和城市名select department_name, city from departments d, locations l where d.location_id = l.location_id and city like '_o%';
sql92.1.5 可以添加分组
case1: 查询每个城市的部门个数select location_id, count(1) as _count from departments group by location_id;
case2:查询有奖金的每个部门的部门名和部门的领导编号和该部门的最低工资select department_name, e.manager_id, min(salary) as _min from employees e, departments d where e.commission_pct is not null group by d.department_id;
sql92.2 非等值连接:
sql92.2.1 demo
case1: 查询员工的工资和工资级别select salary, grade_level from employees e, job_grades g where salary between g.lowest_sal and g.highest_sal;select salary, grade_level from employees e, job_grades g where salary between g.lowest_sal and g.highest_sal and g.grade_level = 'A';
sql92.3 自连接:
sql92.3.1 demo
case1: 查询 员工名和上级的名称select e.employee_id, e.last_name, m.employee_id, m.last_name from employees e, employees m where e.manager_id = m.employee_id;Note
一、sql99标准
语法:select 查询列表 from 表1 别名 [连接类型] join 表2 别名 on 连接条件 [where 筛选条件] [group by 分组] [having 筛选条件] [order by 排序列表 [asc|desc]];
分类:内连接(inner),外连接:左外(left[outer]),右外(right[outer]),全外(full[outer]),交叉连接(cross)
特点:①: 多表等值连接的结果为多表的交集部分②: n表连接,至少需要n-1个连接条件③: 多表的顺序没有要求④: 一般需要为表起别名⑤: 可以搭配前面介绍的所有子句使用,比如排序,分组,筛选。
sql99.1 内连接:
分类:等值,非等值,自连接
特点:①: 添加排序,分组②: inner 可以省略③: 筛选条件放在where后面,连接条件放在on后面,提高分离性,便于阅读④: inner join连接和sql92语法中的等值连接效果是一样的,都是查询多表的交集
sql99.1.1 等值连接
case1: 查询员工名,部门名select last_name, department_name from employees e inner join departments d on e.department_id = d.department_id;
case2: 查询名字中包含e的员工名和工种名(添加筛选)select last_name, job_title from employees e inner join jobs j on e.job_id = j.job_id where e.last_name like '%e%';
case3: 查询部门个数>3的城市名和部门个数(添加分组+筛选)select city, count(1) as _count from departments d inner join locations l on d.location_id = l.location_id group by city having _count > 3;
case4: 查询哪个部门的员工个数>3的部门名和员工个数,并按照个数降序(添加排序)select department_name, count(1) as _count from employees e inner join departments d on e.department_id = d.department_id group by e.department_id having _count > 3 order by _count desc;
case5: 查询员工名,部门名,工种名,并按部门名降序select last_name, department_name, job_title from employees e inner join departments d on e.department_id = d.department_id inner join jobs j on e.job_id = j.job_id order by d.department_name desc;
sql99.1.2 非等值连接
case1: 查询员工的工资级别select last_name, grade_level from employees e inner join job_grades g on e.salary between g.lowest_sal and g.highest_sal;
case1: 查询工资级别个数>2的个数,并按照工资降级排序select grade_level, count(1) as _count from employees e inner join job_grades g on e.salary between g.lowest_sal and g.highest_sal group by grade_level having _count > 20 order by _count desc;
sql99.1.3 自连接
case1: 查询员工的名字,上级的名字select e.last_name, m.last_name from employees e inner join employees m on e.manager_id = m.employee_id;
case1: 查询员工姓名中包含字符k的员工的名字,上级的名字select e.last_name, m.last_name from employees e inner join employees m on e.manager_id = m.employee_id where e.last_name like '%k%';
sql99.2 外连接:
特点:①: 外连接的查询结果为主表中的所有记录(从表中有,则显示,没有显示NULL)②: 左外连接(left join 左边的是主表),右外连接,right join右边的是主表。③: 左外和右外交换两表的顺序,可以实现同样的效果④: 全外连接就是两表的并集(mysql不支持)⑤: 交叉连接(就是sql92中的逗号连接)
case1: 查询没有男朋友的女神select b.id, b.name from beauty b left join boys y on b.boyfriend_id = y.id where y.id is null;
case2: 查询哪个部门没有员工select d.department_name from departments d left join employees e on d.department_id = e.department_id where e.employee_id is null;
case3: 交叉连接select b.*, bo.* from beauty b cross join boys bo;8.子查询 #
含义:出现在其他语句中的select语句,称为
子查询或内查询,内部嵌套其他select语句的查询,称为外查询或主查询。select first_name from employees where department_id in (select department_id from departments where location_id = 1700);
分类:1).按子查询出现的位置:select后面(仅仅支持标量子查询),from后面(支持表子查询),where或having后面(标量子查询,列子查询,行子查询),exists后面(表子查询)2).按结果集的行列数不同:标量子查询(结果集只有一行一列),列子查询(结果集只有一列多行),行子查询(结果集有一行多列),表子查询(结果集一般为多行多列)Note
一、where或者having后面
语法:select 查询列表 from 表 [where (子查询)] [group by 分组] [having (子查询)] [order by 排序列表 [asc|desc]];
特点:①: 子查询放在小括号内②: 子查询一般放在条件的右侧③: 标量子查询一般搭配着单行操作符使用:>, <, >=, <=, =, <>,列子查询一般搭配着多行操作符时候用:in, any/some, all④: 子查询的执行优先于主查询的执行,主查询的条件用到了子查询的结果。
非法使用标量子查询(1,不是一行一列,2,干脆没有值)
1. 标量子查询:
case1: 谁的工资比Abel高select * from employees where salary > (select salary from employees where last_name = 'Abel');
case2: 返回iob_id 与 141 号员工相同,salary 比 143号员工多的员工的姓名,job_id 和工资select last_name, job_id, salary from employees where job_id = (select job_id from employees where employee_id = 141) and salary > (select salary from employees where employee_id = 143);
case3: 返回公司工资最少的员工的last_name, job_id 和 salaryselect last_name, job_id, salary from employees where salary = (select min(salary) from employees);
case4: 查询最低工资大于 50号部门的最低工资 的部门的部门Id 和 其最低工资select department_id, min(salary) as _min from employees group by department_id having _min > (select min(salary) from employees where department_id = 50);
2. 列子查询(多行子查询):
case1: 返回location_id是1400或1700 的部门中的所有员工姓名select last_name from employees where department_id in (select distinct department_id from departments where location_id in(1400, 1700));
case2:返回其他部门中比job_id 为’IT_PROG’部门任意工资低的 员工的工号,姓名,job_id以及salary。
case2: 返回其他工种中比job_id 为’IT_PROG’工种任意工资低的 员工的工号,姓名,job_id以及salary。select employee_id, last_name, job_id, salary from employees where job_id <> 'IT_PROG' and salary < (select max(salary) from employees where job_id = 'IT_PROG');
case2: 返回其他工种中比job_id 为’IT_PROG’工种所有工资低的 员工的工号,姓名,job_id以及salary。select employee_id, last_name, job_id, salary from employees where job_id <> 'IT_PROG' and salary < (select min(salary) from employees where job_id = 'IT_PROG');
3. 行子查询(结果集一行多列或多行多列):
case1: 查询员工编号最小并且工资最高的员工信息select * from employees where (employee_id, salary) = (select min(employee_id), max(salary) from employees);Note
二、select后面
case1: 查询每个部门的个数select d.*, (select count(1) from employees e where e.department_id = d.department_id) from departments d;
case2:查询员工号 = 102 的部门名Note
三、from后面
要求:将子查询结果充当一张表,要求必须起别名
case1: 查询每个部门的平均工资的工资等级select temp.*, jg.grade_level from (select department_id, avg(salary) as _avg from employees group by department_id) temp inner join job_grades jg on temp._avg between lowest_sal and highest_sal;Note
四、exists后面(相关子查询)
语法:select exists(完整的查询语句),结果 1或0
case1: 查询有员工的部门名select department_name from departments d where exists (select * from employees e where e.department_id = d.department_id);select department_name from departments d where department_id in (select department_id from employees);
case2: 查询没有女朋友的男神信息select bo.* from boys bo where not exists (select * from beauty b where b.boyfriend_id = bo.id);select bo.* from boys bo where bo.id not in (select boyfriend_id from beauty);9.分页查询 #
语法:
select 查询列表 from 表 [where 筛选条件] [order by 排序列表 [asc|desc]] limit [[offize,] size];
特点:1).limit语句放在整个查询语句的最后。2).公式:page, size ==> limit (page - 1) * size, size
case1: 查询前5条员工的信息select * from employees limit 0, 5;select * from employees limit 5;
case2: 查询第11条到25条select * from employees limit 10, 15;
case3: 有奖金的员工信息,并且工资较高的前10名显示出来select * from employees where commission_pct is not null order by salary desc limit 10;10.联合查询 #
语法:
() union () union () ...
将多条查询语句的结果合并成一个结果
特点:1).要求多条查询语句的查询列数是一致的2).要求多条查询语句的每一列的类型和顺序最好一致3).union关键字默认去重,如果使用union all可以包含重复项
case1: 查询部门编号 >90 或 邮箱中包含a的员工的信息select * from employees where email like '%a%' union select * from employees where department_id > 90;
case1: 查询中国用户中男性的信息以及外国用户中男性的信息select id, cname, csex from t_ca where csex = '男' union select t_id, tName, tGender from t_ua where tGender = 'male';