THREAD-POOL
Intro(THREAD POOL) #
ThreadPoolExecutor.java
线程池解决了两个不同的问题:1).在执行大量异步任务时,由于减少了每个任务的调用开销,它们通常提供改进的性能;2).在执行一组任务时,它们提供了一种绑定和管理资源(包括线程)的方法。每个ThreadPoolExecutor还维护一些基本统计信息,例如已完成任务的数量。核心和最大线程数:
线程池会根据核心线程数和最大线程数自动调节池中的线程数量。当一个任务提交的时候,如果少于核心线程数的线程正在运行,则一个新的线程被创建用来处理当前的任务请求(即使其它线程空闲)。如果运行的线程数在核心线程和最大线程之间,则优先队列任务,如果队列满了,就创建线程。队列(BlockingQueue):
队列用来传输和持有提交的任务,它的使用和线程池中的线程数互相作用。有以下几点:a).小于核心线程数的线程正在运行,则创建新线程。b).大于核心线程数,则入队列c).入队列不成功(满了),但是小于最大线程数,则创建新线程。d).其他情况(队列满了且达到最大线程数),则拒绝执行。
对于队列的选择,一般有三种情况:SynchronousQueue:这个阻塞队列的特性是,每插入一个元素,必须消费之后才可以继续插入。而且可以支持公平和非公平选择,用于对等待的生产者和消费者线程进行排序。所以使用这种队列,如果在生产速度大于消费速度,则通过queue.offer()方法放不进去,只能创建新线程进行处理了。所以线程数可能无限增长。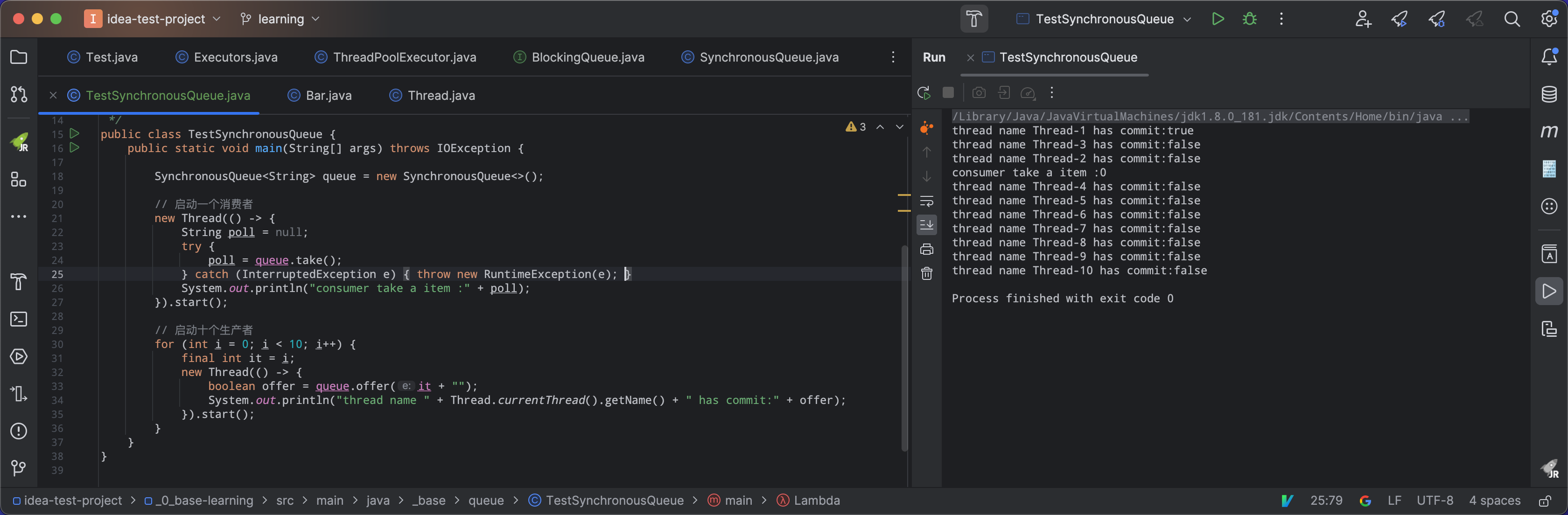
LinkedBlockingQueue:偏无界队列(Integer.MAX_VALUE)ArrayBlockingQueue:有边界
钩子方法:beforeExecute(Thread, Runnable)、afterExecute(Runnable, Throwable)
按需加载:prestartCoreThread(启动一个核心线程)、prestartAllCoreThreads(启动所有核心线程)属性 #
ctl 是一个原子整数类型,里面主要体现两个属性:
workerCount: 有效的线程数量、runState: 是否运行,关闭等状态。
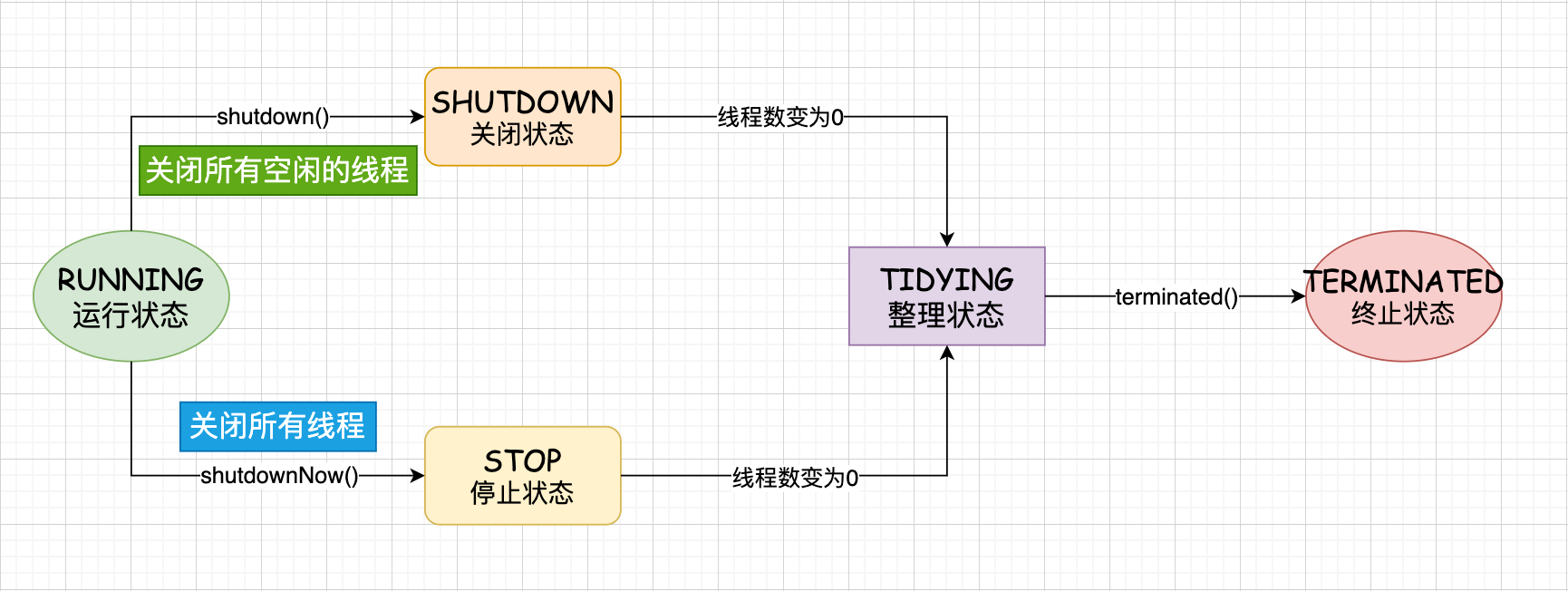
为了将这两个属性放在一个数字里面控制,我们限制了workerCount的值为 \({\color{blue}(2^{29} - 1 )}\)(大约5亿个线程),而不是 \({\color{blue} (2^{31} - 1)}\)(大约20亿)workerCount:允许开始执行的线程数。因为一些原因,这个值可能和实际存活的线程数暂时不一致,比如:当要求线程池创建线程的时候失败了,或者在terminated之前退出线程依旧在执行任务。runState:线程池状态RUNNING: 可以接受新的任务并且处理队列中的任务SHUTDOWN: 不接受新的任务但是会处理队列中的任务STOP: 不接受新的任务,不处理队列中的任务,并且给中断正在执行的线程TIDYING: 所有任务都已种植,workerCount 为零,转换到 TIDYING 状态的线程将执行terminated()钩子方法。TERMINATED:terminated()钩子方法执行完毕。
为了允许有序比较,这些值之间的数字顺序很重要。runState单调地随时间增加,但不需要达到每个状态。转换过程:Caution
下面代码中的属性值转换成十进制没有任何意义,所以直接使用二进制计算就行。
连续多个 0、1 简写:使用括号,里面是个数及值,中间用|分割。比如(29|0)表示连续 29个0,(28|1)表示连续 28个1 。方法 #
状态转换 #
定义 #
创建 #
种类 #
Reference #