AQS
AQS 内部结构 #
内部类Node节点代码
代码示例
static final class Node { /** Marker to indicate a node is waiting in shared mode */ static final Node SHARED = new Node(); /** Marker to indicate a node is waiting in exclusive mode */ static final Node EXCLUSIVE = null; /** waitStatus value to indicate thread has cancelled */ static final int CANCELLED = 1; /** waitStatus value to indicate successor's thread needs unparking */ static final int SIGNAL = -1; /** waitStatus value to indicate thread is waiting on condition */ static final int CONDITION = -2; /** * waitStatus value to indicate the next acquireShared should * unconditionally propagate */ static final int PROPAGATE = -3; /** * Status field, taking on only the values: * SIGNAL: The successor of this node is (or will soon be) * blocked (via park), so the current node must * unpark its successor when it releases or * cancels. To avoid races, acquire methods must * first indicate they need a signal, * then retry the atomic acquire, and then, * on failure, block. * CANCELLED: This node is cancelled due to timeout or interrupt. * Nodes never leave this state. In particular, * a thread with cancelled node never again blocks. * CONDITION: This node is currently on a condition queue. * It will not be used as a sync queue node * until transferred, at which time the status * will be set to 0. (Use of this value here has * nothing to do with the other uses of the * field, but simplifies mechanics.) * PROPAGATE: A releaseShared should be propagated to other * nodes. This is set (for head node only) in * doReleaseShared to ensure propagation * continues, even if other operations have * since intervened. * 0: None of the above * * The values are arranged numerically to simplify use. * Non-negative values mean that a node doesn't need to * signal. So, most code doesn't need to check for particular * values, just for sign. * * The field is initialized to 0 for normal sync nodes, and * CONDITION for condition nodes. It is modified using CAS * (or when possible, unconditional volatile writes). */ volatile int waitStatus; /** * Link to predecessor node that current node/thread relies on * for checking waitStatus. Assigned during enqueuing, and nulled * out (for sake of GC) only upon dequeuing. Also, upon * cancellation of a predecessor, we short-circuit while * finding a non-cancelled one, which will always exist * because the head node is never cancelled: A node becomes * head only as a result of successful acquire. A * cancelled thread never succeeds in acquiring, and a thread only * cancels itself, not any other node. */ volatile Node prev; /** * Link to the successor node that the current node/thread * unparks upon release. Assigned during enqueuing, adjusted * when bypassing cancelled predecessors, and nulled out (for * sake of GC) when dequeued. The enq operation does not * assign next field of a predecessor until after attachment, * so seeing a null next field does not necessarily mean that * node is at end of queue. However, if a next field appears * to be null, we can scan prev's from the tail to * double-check. The next field of cancelled nodes is set to * point to the node itself instead of null, to make life * easier for isOnSyncQueue. */ volatile Node next; /** * The thread that enqueued this node. Initialized on * construction and nulled out after use. */ volatile Thread thread; /** * Link to next node waiting on condition, or the special * value SHARED. Because condition queues are accessed only * when holding in exclusive mode, we just need a simple * linked queue to hold nodes while they are waiting on * conditions. They are then transferred to the queue to * re-acquire. And because conditions can only be exclusive, * we save a field by using special value to indicate shared * mode. */ Node nextWaiter; /** * Returns true if node is waiting in shared mode. */ final boolean isShared() { return nextWaiter == SHARED; } /** * Returns previous node, or throws NullPointerException if null. * Use when predecessor cannot be null. The null check could * be elided, but is present to help the VM. * * @return the predecessor of this node */ final Node predecessor() throws NullPointerException { Node p = prev; if (p == null) throw new NullPointerException(); else return p; } Node() { // Used to establish initial head or SHARED marker } Node(Thread thread, Node mode) { // Used by addWaiter this.nextWaiter = mode; this.thread = thread; } Node(Thread thread, int waitStatus) { // Used by Condition this.waitStatus = waitStatus; this.thread = thread; } }整体结构图
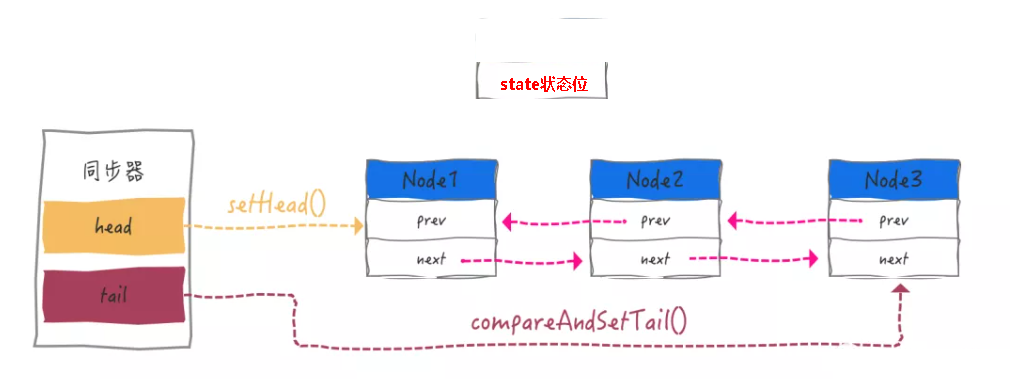
ReentrantLock #
创建ReentrantLock示例
// 新建 ReentrantLock public ReentrantLock() { sync = new NonfairSync(); } // 调用 lock()方法,内部实质是 调用 非公平锁的lock方法。 public void lock() { sync.lock(); }非公平锁与公平锁
获取锁图例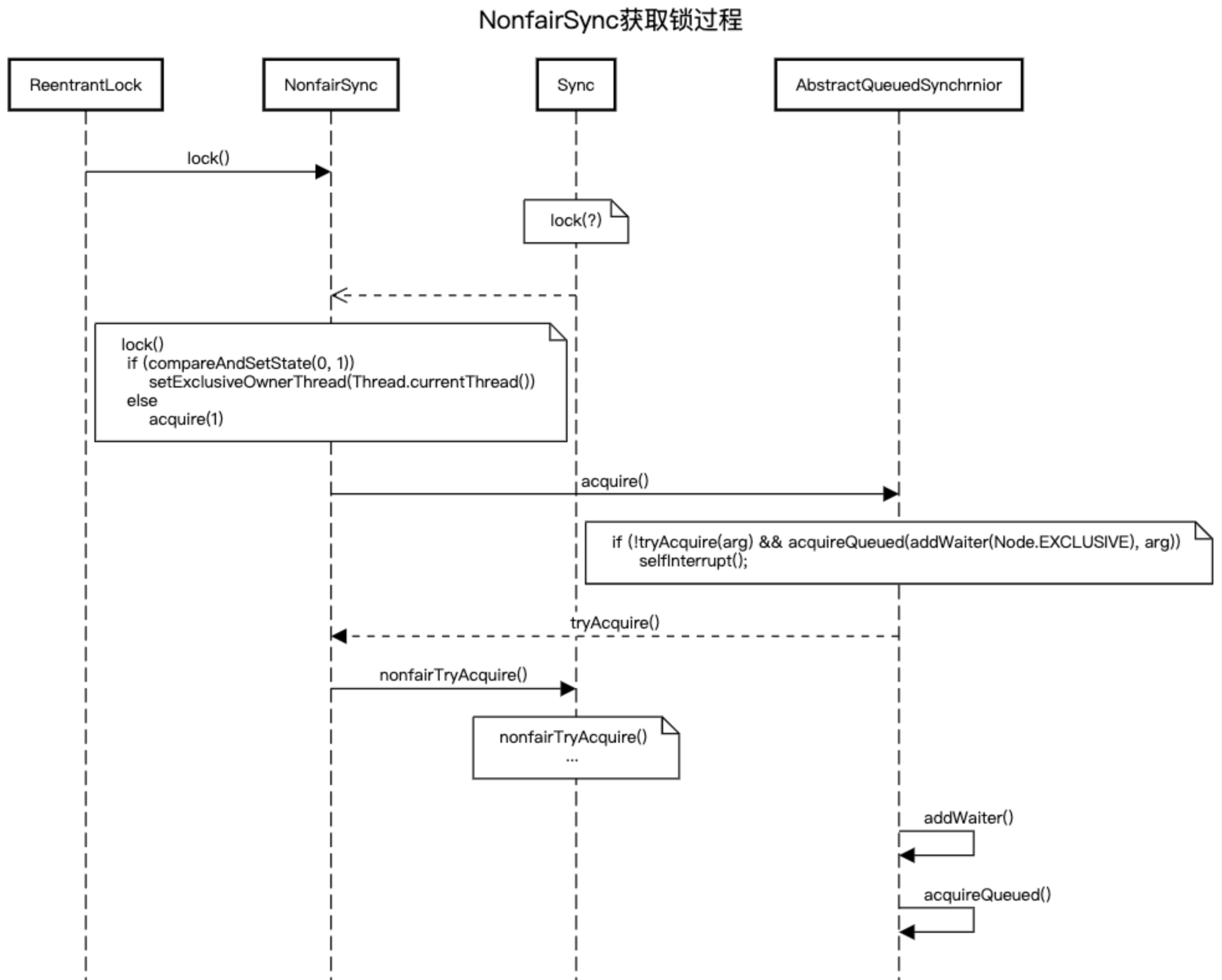
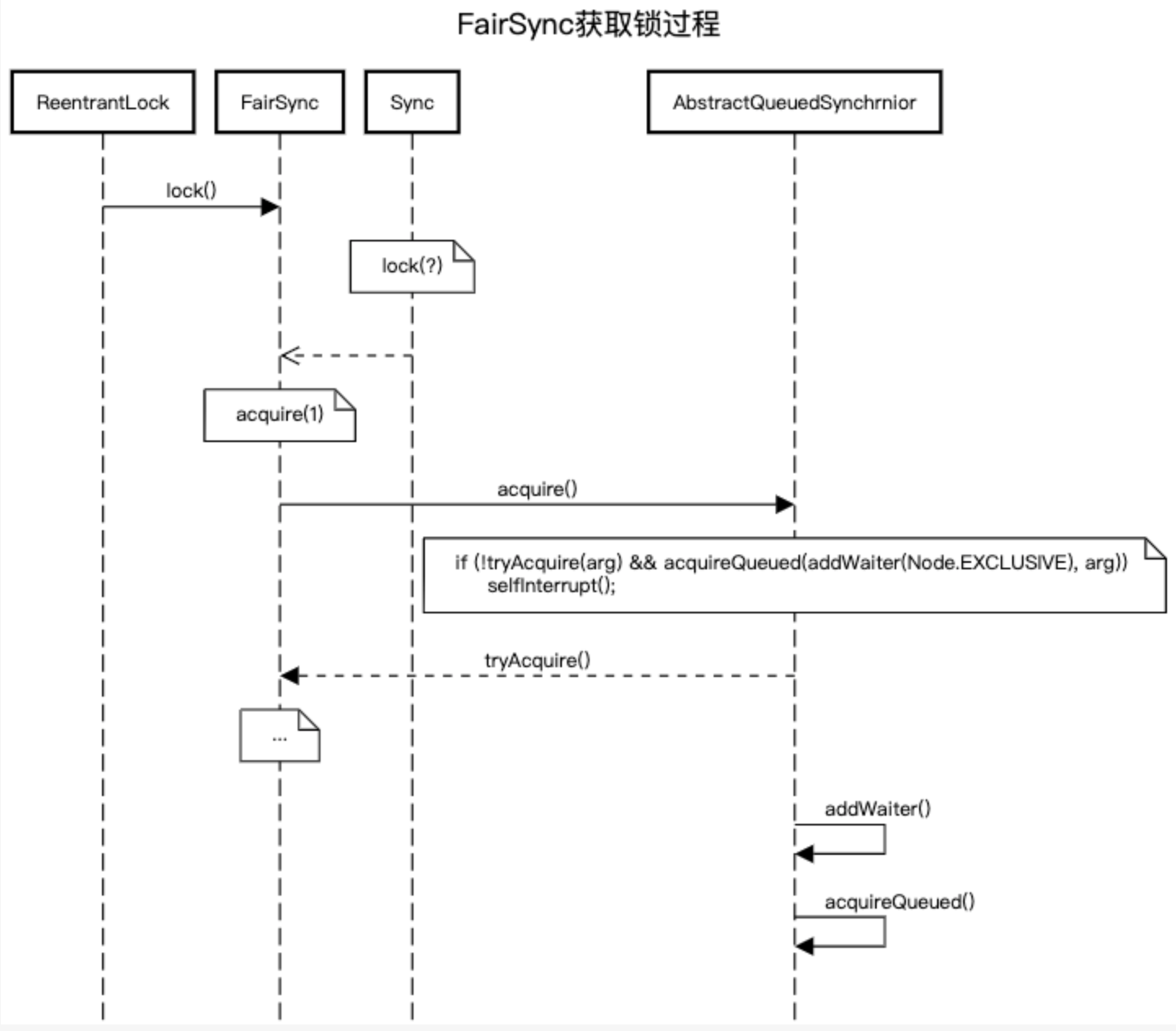
代码片段
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) { final Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); int c = getState(); if (c == 0) { if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) { setExclusiveOwnerThread(current); return true; } } else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) { int nextc = c + acquires; if (nextc < 0) // overflow throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded"); setState(nextc); return true; } return false; }private Node addWaiter(Node mode) { Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode); // Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure Node pred = tail; if (pred != null) { node.prev = pred; if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) { pred.next = node; return node; } } enq(node); return node; } private Node enq(final Node node) { for (;;) { Node t = tail; if (t == null) { // Must initialize if (compareAndSetHead(new Node())) tail = head; } else { node.prev = t; if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) { t.next = node; return t; } } } }final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) { boolean failed = true; try { boolean interrupted = false; for (;;) { final Node p = node.predecessor(); if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) { setHead(node); p.next = null; // help GC failed = false; return interrupted; } if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && parkAndCheckInterrupt()) interrupted = true; } } finally { if (failed) cancelAcquire(node); } } private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() { LockSupport.park(this); return Thread.interrupted(); }/** * Convenience method to interrupt current thread. */ static void selfInterrupt() { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); }protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) { final Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); int c = getState(); if (c == 0) { if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() && compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) { setExclusiveOwnerThread(current); return true; } } else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) { int nextc = c + acquires; if (nextc < 0) throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded"); setState(nextc); return true; } return false; }非公平锁与公平锁
释放锁图例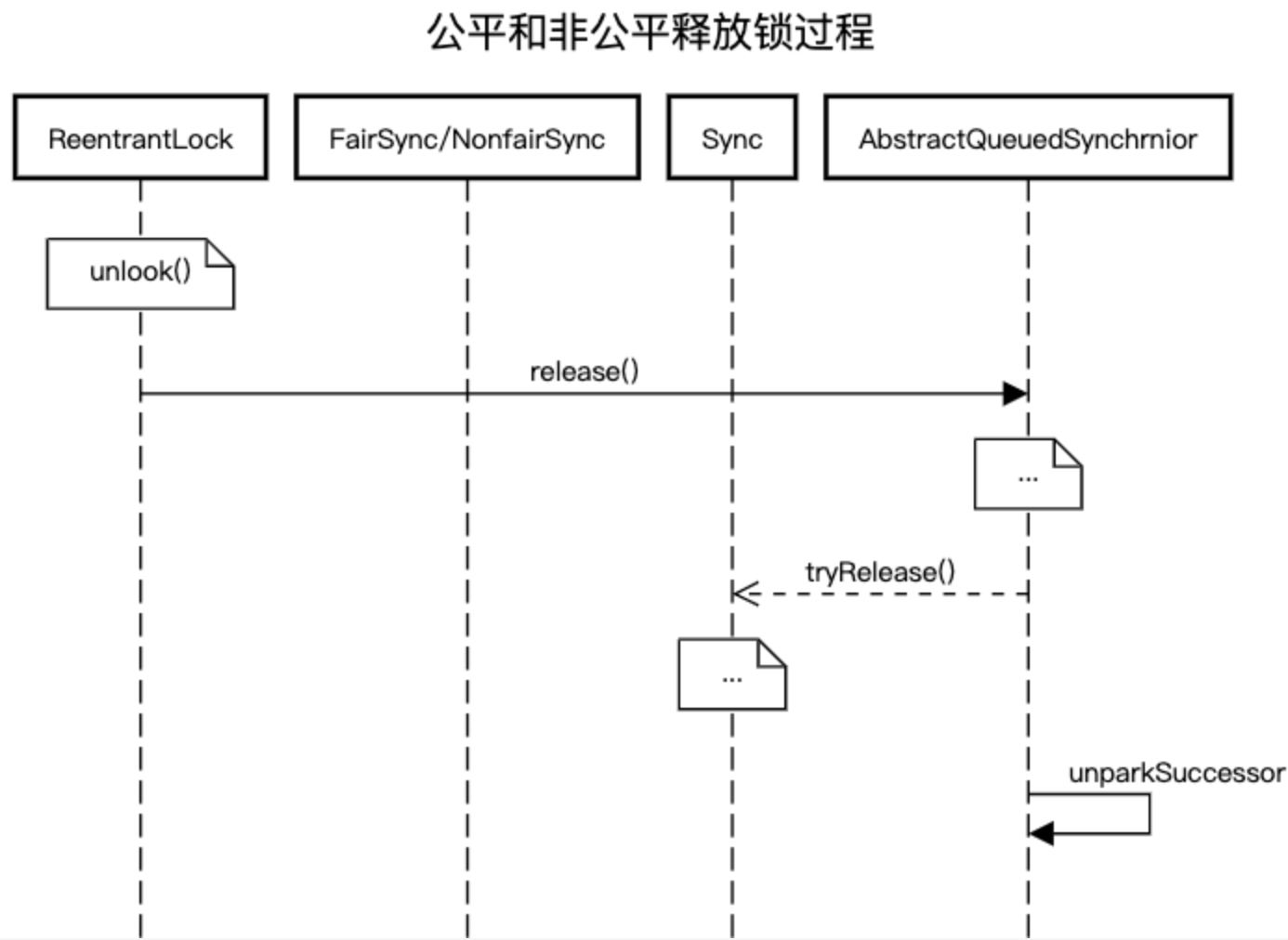
public final boolean release(int arg) { if (tryRelease(arg)) { Node h = head; if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0) unparkSuccessor(h); return true; } return false; } private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) { /* * If status is negative (i.e., possibly needing signal) try * to clear in anticipation of signalling. It is OK if this * fails or if status is changed by waiting thread. */ int ws = node.waitStatus; if (ws < 0) compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0); /* * Thread to unpark is held in successor, which is normally * just the next node. But if cancelled or apparently null, * traverse backwards from tail to find the actual * non-cancelled successor. */ Node s = node.next; if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) { s = null; for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev) if (t.waitStatus <= 0) s = t; } if (s != null) LockSupport.unpark(s.thread); }protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) { int c = getState() - releases; if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread()) throw new IllegalMonitorStateException(); boolean free = false; if (c == 0) { free = true; setExclusiveOwnerThread(null); } setState(c); return free; }
Reference #
comments powered by Disqus